N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), as a disinfection byproduct of chlorination/chloramination and ozonation processes in drinking water and wastewater treatments, cannot be effectively removed from water by physical, chemical and biological methods, because of its small molecular weight and size, high polarity, water solubility and toxicity.
Doctor He Yuanzhen successfully applied the technology of sorptive removal of NDMA from aqueous solution by microporous minerals followed by destruction of the sorbed NDMA by microwave irradiation. Her research investigates the sorptive removal of NDMA from aqueous solution by porous minerals followed by destruction of the sorbed NDMA and its precursor dimethylamine (DMA) by microwave irradiation (figure 1). Sorption of NDMA on porous minerals with different pore sizes, surface cation density and type from water and microwave-induced degradation of the sorbed NDMA were studied. As a result, Na-ZSM-5 (Si/Al=25) appears to be the best mineral sorbent for removing NDMA (along with DMA). Based on the detection and analysis of NDMA degradation products, the technology can transform NDMA to less harmful and small molecular degradation products, and completely eliminate secondary pollution of existing treatment options for NDMA removal and the regeneration of NDMA.
In addition, the degradation products detected suggest that NDMA degradation occurs via the mechanism of pyrolysis caused by formation of micro-scale “hot spots” within surface cations and polar molecules of mineral micropores under microwave irradiation.
This paper has been published in Water Research on 1st May, 2016 (He, Yuanzhen; Cheng, Hefa. Degradation of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) and its precursor dimethylamine (DMA) in mineral micropores induced by microwave irradiation. WATER RESEARCH, 2016, 94: 305-314. DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.02.065)
This work was supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41472324 and 41322024), and the National Program for Support of Top-notch Young Professionals.
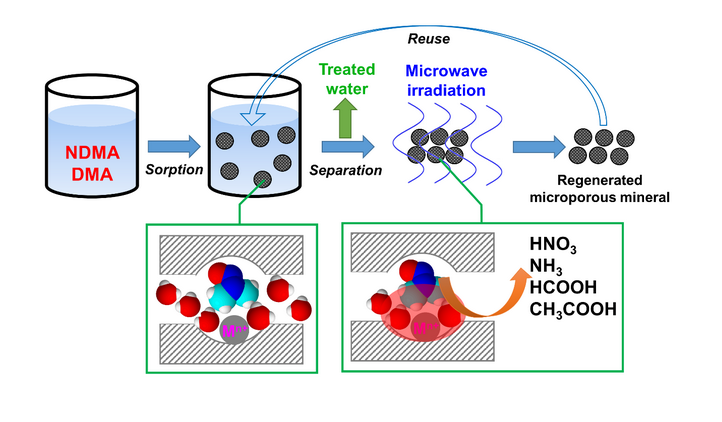
Figure 1. The sorptive removal of NDMA and DMA from aqueous solution by microporous minerals followed by destruction by microwave irradiation (Image by HE Yuanzhen)
Contact:
Doctor HE Yuanzhen
Email: heyuanzhen@gig.ac.cn