Recently, Prof. LUO Chunling’s research team in Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (GIGCAS), explored the functional populations actually responsible for in situ phenanthrene (PHE) degradation in petroleum-contaminated wastewater using DNA-stable isotope probing (SIP) and high-throughput sequencing.
According to the SIP results, besides the well-known PHE degraders Acinetobacter and Sphingobium, Kouleothrix and Sandaracinobacter were found, for the first time, to be directly responsible for indigenous PHE biodegradation. Compared with those of pure cultures, a novel representative active PHE degrader (Acinetobacter tandoii LJ-5) was successfully identified and isolated from the indigenous wastewater microbial community. LJ-5 exhibited a extreme high efficiency for PHE biodegradation, and it could possibly use the β-ketoadipate pathway to degrade PHE and other aromatic compounds.
This research provides a successful technological demonstration for the in situ exploration and isolation of functional microorganisms. At present, the research team is working on the development of LJ-5 to be an applicable agent in the in situ bioremediation of petroleum contaminated sites. Moreover, study on the interaction mechanism of this strain and other microbial bacteria within the complex microbial communities is going on, which would be helpful to reach an ideal remediation efficiency under the in situ conditions.
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the results were recently published in Environmental Science & technology.
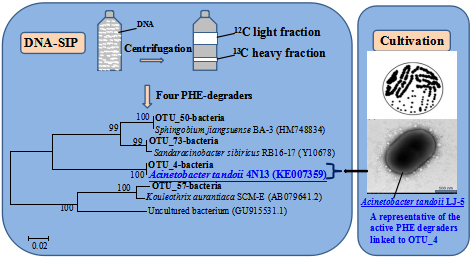
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of identification of functional microorganisms by DNA-SIP and pure culture. (Image by LUO Chunling)

Figure 2 Phylogenetic tree of identified OTUs (OTU_4, OTU_50, OTU_73 and OTU_57) responsible for PHE degradation.(Image by LUO Chunling)
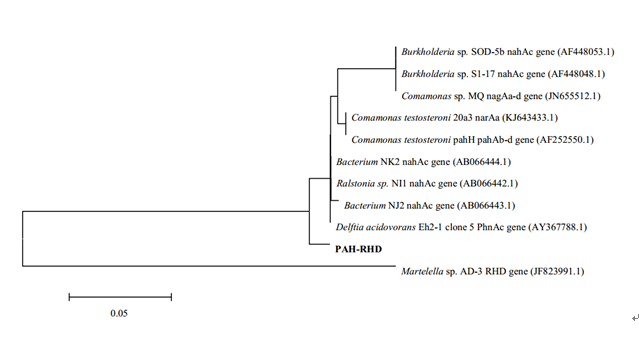
Figure 3 Phylogenetic analysis of amplified PAH-RHDα GN gene based on the amino acid sequences from heavy fraction in 13C-PHE microcosm. (Image by LUO Chunling)
Contact:
Prof. LUO Chunling
clluo@gig.ac.cn